ALUMINUM COATING TIN-LEAD
Description
Tin-lead coating is related to tin-bismuth and has a higher the percentage of alloying additive (in this case, lead) in the alloy. The standard potentials of tin and lead are close (-0.136 and -0.126 V, respectively), so they are galvanically deposited from solutions of simple salts. Lead and tin do not form either solid solutions or chemical compounds. The structure of the coating is a mechanical mixture of crystals of these metals. The introduction of lead gives the coating such important properties as frost resistance and softness, but the shiny appearance of the surface becomes unattainable. Most often it has a gray color, sometimes non-uniform, especially on complex surfaces. The coating is initially quite rough and porous, which can be eliminated by additional processing, for example, melting.
Tin-lead alloy coatings are used to protect products from corrosion in sea water and other aggressive environments. The alloy can be deposited in a wide range of compositions. The coating with a lead content of 50% has the greatest chemical resistance. Alloys with a tin content of 5 to 17% are used as anti-friction alloys, especially in combination with oils. The universal composition is considered to be 60% Sn and 40% Pb by weight (analogous to Gor.POS 60).
You can order tinning of aluminum with a tin-lead alloy in accordance with GOST 9.305-84 by phone and email indicated in the section "CONTACTS".
Characteristics
|
Designation (examples) |
Sn-Pb |
|
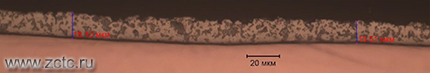
Thickness |
9-100 microns (greater thickness is possible) |
|
Microhardness |
118-198 MPa |
|
Electrical resistivity at 18° C |
11.5⋅10-8 Ohm⋅m (inaccurate data) |
|
Permissible operating temperature |
200° C |
|
Lead content in Sn-Pb alloy |
60% |
Advantages of tin plating:
- Tin-lead coating (Sn-Pb) is cathodic to aluminum under atmospheric conditions and protects it mechanically.
- Excellent soldering using low-temperature solders.
- More ductile than tin-bismuth.
- The tin-lead alloy is soft and has excellent anti-friction characteristics.
- It has low electrical resistance and is suitable for use in electrical products: lugs, clamps, busbars, to protect contacting current-carrying surfaces from oxidation or contact with metals, which results in the formation of a galvanic couple (copper-aluminum, steel-copper).
- The fused tin-lead coating is not subject to the phenomenon of needle formation.
Disadvantages of tin plating:
- Cannot be used on parts in contact with food due to lead toxicity.
- At high temperature and high humidity, the corrosion resistance of tin-lead alloy is lower than that of tin coating or tin-bismuth alloy.
- After crimping a tin-lead alloy into polymer materials, solderability needs to be restored hot using non-activated rosin flux.
- The coating is non-decorative. Without brushing, uneven matt gray color and high roughness

Do you want to become our client?
Just leave your request by filling out the form on the right and we will contact you as soon as possible. Thank you!

By submitting an application, you agree to processing of your personal data. Your data is protected.





